Retailers are constantly looking for new ways to generate revenue and stay competitive. One strategy …
How SymmetricDS Pro Enhances Security

Deploying SymmetricDS in an enterprise environment with critical business data means information security is important. Let’s take a look at how the professional edition of SymmetricDS enhances security with authentication, access control, encryption, and auditing.
Authentication
The web console makes it easy to manage data replication, but we also need it to be secure. The Configure → Users screen lets you setup local users or users based on LDAP or ActiveDirectory. Password strength is checked by a complexity meter, which is displayed to the user as they type. Password requirements help ensure strong passwords. Requirements include minimum length, alpha numeric, symbols, mixed cased, non-common words, and prohibit matching against previous passwords. Rotation of passwords can also be enforced, causing expiration and changing of passwords every number of days.
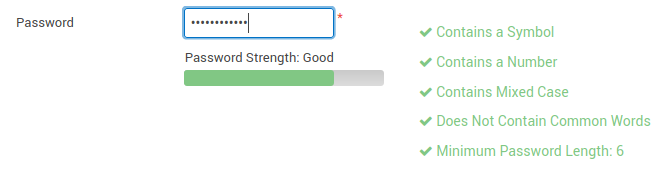 Figure 1: Password complexity meter shows if you’ve met requirements for a strong password.
Figure 1: Password complexity meter shows if you’ve met requirements for a strong password.
During login, a delay is added for a bad attempt to slow down brute force. After 5 failed attempts, the account is disabled and needs an admin to re-enable it. After a successful login, the last login time and IP address are shown to the user. The overall number of sessions is limited, and each user is allowed 1 session. After 30 minutes, the session times out and the user is logged out automatically.
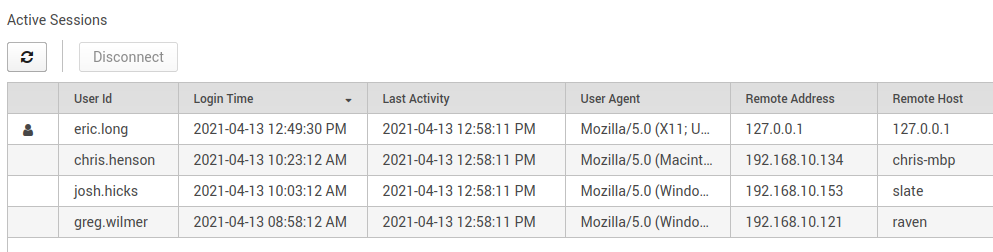 Figure 2: Viewing sessions of who’s logged in and from where.
Figure 2: Viewing sessions of who’s logged in and from where.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) can be enabled for an extra layer of security on top of login credentials. SymmetricDS Pro uses a time-based one-time password (TOTP) system that is compatible with Google Authenticator. On the first login, the user will scan a barcode from their smartphone to store a shared secret. For future logins, the user provides their username and password, and then enters a six-digit password from their smartphone.
Access Control
Access control is selective restriction of access to data. SymmetricDS allows each user to belong to a role, with each role given a group of privileges. Based on the principle of “least privilege”, the role-based access control gives users the privilege of accessing only the data that is necessary for their role. From the Configure → Roles screen, any number of custom roles can be created and granted privileges. Privileges can be assigned at the levels of tab, screen, and operation to allow as much or as little granularity as needed. For example, an “installer” role can be created that has only the privilege to add nodes to the data replication.
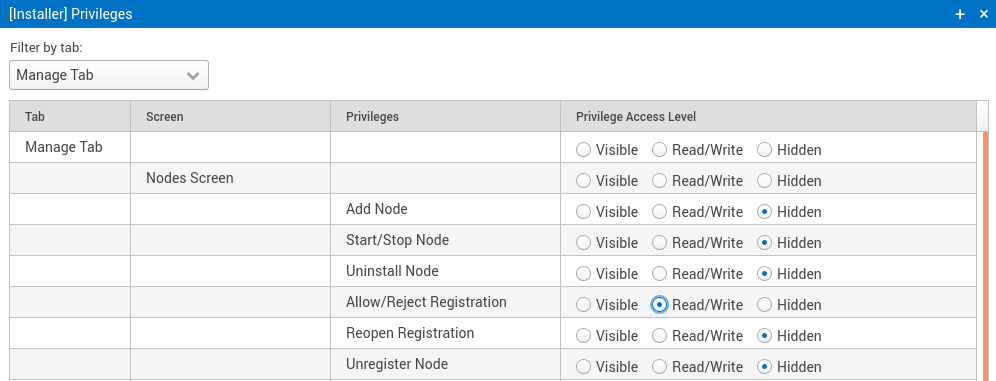 Figure 3: Setting privileges for the role of a user who will be able to register new nodes.
Figure 3: Setting privileges for the role of a user who will be able to register new nodes.
Encryption
SymmetricDS Pro uses encryption to protect sensitive data during transfer and when it’s at rest. The following are some examples of data protection.
- User credentials
- Passwords are one-way hashed as SHA-512 and stored in the database with salt to resist brute force attempts.
- Node passwords
- Nodes have passwords too (random 30-characters) that are encrypted with AES-256 in the database.
- Database credentials
- The database username and password are encrypted with AES-256.
- Data transfer
- Both users of the web console and transfer of data replication is over web-based HTTPS with TLS 1.2.
- Data staging
- The staging area where data is shuttled in and out of the database is encrypted with AES-256.
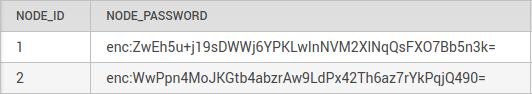 Figure 4: Node passwords that are prefixed with “enc:” were encrypted to hide them from prying eyes.
Figure 4: Node passwords that are prefixed with “enc:” were encrypted to hide them from prying eyes.
Auditing
An effective audit log enables compliance, accountability, and security. SymmetricDS Pro has an audit log for actions taken by users and any changes they make to the system. It provides filtering of the events, which can then be exported to a report. Audit logs help with compliance with regulations like HIPAA and PCI DSS because the records can be shared with auditors to protect the business from fines or penalties. They help with accountability because they show what actions took place, when they occurred, and who was responsible for them. They help with proactively monitoring for security problems, then tracking down a breach with evidence for investigators.
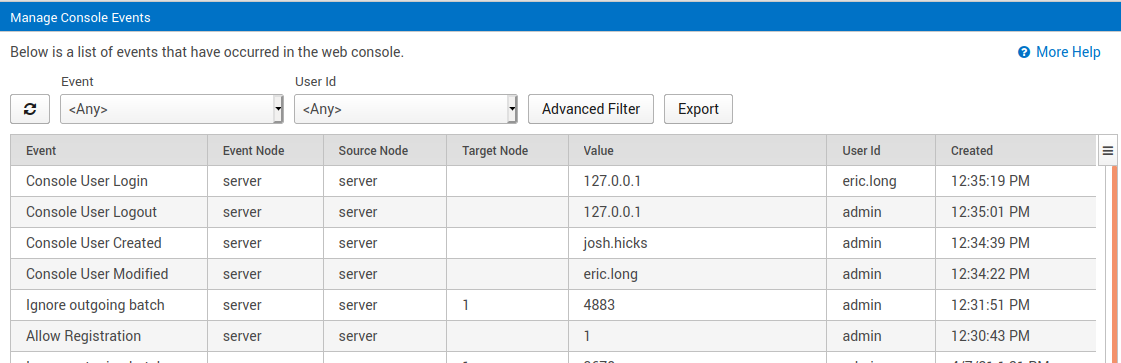 Figure 5: Audit reporting of user events to confirm authorized activities.
Figure 5: Audit reporting of user events to confirm authorized activities.
Summary
Security is important because it protects a business from liability, compliance, damage to its reputation, and exposure of secrets. The domino effect of a security breach could lead to financial problems and ruin of a company. Show your customers, employees, and shareholders that you care enough to protect the business. Consider using SymmetricDS Pro for data replication because it’s enhanced with authentication, access control, encryption, and auditing which are fundamentals for good enterprise security.