Physical retail is still where the magic happens. According to new research by RSR, 85% …
![]()
Cloud-native POS platform for seamless omnichannel customer experience.
![]()
A single hub for all promotions campaigns.
- Omnichannel ExperienceCreate seamless customer experiences
- Device IndependencePOS agnostic to form factor or operating system
- Self-CheckoutDo more with fewer associates
- Mobile StoreLeverage POS from anywhere
- POS on the GoEnable associates to sell outside of the store
- Unified PromotionsStreamline and simplify promotion workflows
- CX ConnectAllow customers to engage with POS during checkout
- Composable CommerceCreate the store experience you want
![]()
The most advanced synchronization solution for databases and file systems.
![]()
Data configuration and batch automation across different disparate systems and vendors.
-
Data Replication
- Multi-tier DistributionReplicate thousands of remote locations
- Cloud Database ReplicationCapture live changes from on-premise to the cloud
- High Availability and Load BalancingEnsure 24/7 access to data and scale efficiently with demand
- Analytics and ReportingCapture the whole picture with real-time reporting
- Multi-masterMaintain consistency of data in a peer to peer setup
- Data WarehouseReplicate live and historical data to a warehouse
- MigrationsConduct live data migration with no downtime
-
-
Data Integration
- Master Data ManagementChanges propagate across the entire system, allowing you to maintain a centralized view of all parts of your core business entities.
- Application IntegrationReduce dependencies, complexity, and risk to build a high-performance, data-driven application.
- Web ServicesIntegrate multiple systems using web services or build a business application using a service-oriented architecture.
- Data WarehouseIntegrate disparate data from multiple systems so you can transform data for better business intelligence and reporting.
- Data MigrationConduct live data migration during critical server replacements, storage upgrades, and data center relocations—with no downtime.
- ImplementationIntegration consultants help design, develop, and deploy an implementation of our products.
- DevelopmentThe product developers can add features, enhance existing functionality or build support for new platforms.
- TrainingEngage our experienced training resources to gain in-house knowledge and expertise on Jumpmind products.
- SupportLeverage product engineers to resolve issues, fix defects and provide updates or patches.
- Proof of ConceptDetermine the feasibility of implementing our products and get answers to your questions quickly.
Beyond the Hype: What Retailers Really Want from Tech in 2025 Europe’s biggest retail conference …
What a fun week it was for women from across the country who came together …
View all Blog Posts
The new release of SymmetricDS Pro 3.16 data replication software simplifies setup, improves performance, and …
Sybase ASE (more recently known as SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise), announced its end of mainstream …
Azure Blob Storage has become a popular option for storing files in the cloud. And …
View all Blog Posts
Jumpmind Powers Point of Sale and Promotions Execution for Landmark Retail, One of the Largest …
Retail Technology Leader Jumpmind to Enable Mobile Point of Sale and Inventory Management for DTLR/VILLA …
The retailer is charting its next chapter with retail technology modernization to power inspired omnichannel …
View all Customer Stories
43 percent say handling online order returns in-store is a top challenge, and that increases …
After nearly a century in business, the legendary Canadian fashion retailer is retooling to streamline …
The Solution Addresses Modern Retail Challenges with Innovative Promotions to Captivate Inflation-Weary Shoppers NRF 2024, …
View all Blog Posts
![]()
Cloud-native POS platform for seamless omnichannel customer experience.
![]()
A single hub for all promotions campaigns.
![]()
The most advanced synchronization solution for databases and file systems.
![]()
Data configuration and batch automation across different disparate systems and vendors.
-
Data Replication
-
-
Data Integration
-
Retail Retail trends, technology, and enhancing the customer experience
-
Data Thoughts on data matters, dialects, performance, and security
-
Customer Stories How Jumpmind impacts the businesses of our clients
-
Videos & Webinars Watch on demand demos, reviews, and tours of our products
-
Company News Get the scoop on Jumpmind's growth and impact
View all Blog Posts
Verify Data Replication with Compare and Repair

Compare and Repair for SymmetricDS Pro can compare two databases, report on the differences, and repair the data without interrupting uptime. It works cross-platform between any supported databases, uses parallel threads for performance, and minimizes network traffic. Let’s look at how compare and repair works and why it is required by some businesses.
Find Data Differences
Using the Manage -> Compare screen in the SymmetricDS Pro web console, the user can request a comparison between two remote databases. Requests can run immediately or be scheduled for a date and time. The user chooses which tables to compare , how to detect changes, and how to report or repair them. Differences can be detected quickly by row counts or more accurately using a checksum. The precision of comparison on decimals, floating points, and timestamps can be restricted to work across different database platforms. For a system that is undergoing changes, in-flight data can be used so it’s not miscounted as differences.
Report and Repair Data
The reporting level can be selected for a quick report or more detailed report. The first level report lists each table and whether it matched or not. The second level report counts rows that are matching, different, missing, or extra. Finally, the most detailed report includes data differences as a SQL script with insert, update, and delete statements to repair the target database. Afterwards, the user can choose to have the repair script applied automatically to the target database.
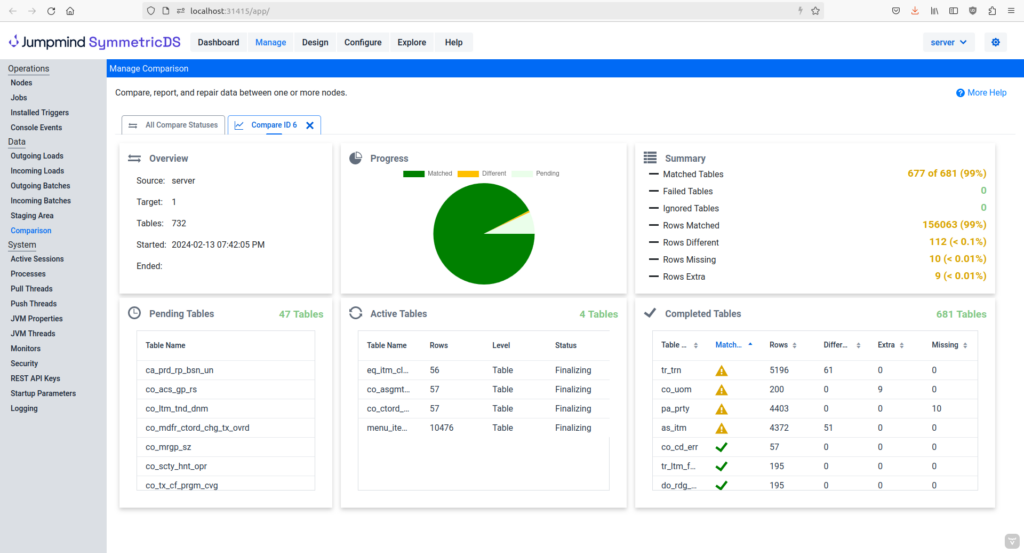
How Data Verification Works
Compare and repair works across the existing HTTP/S links that SymmetricDS Pro uses for data replication. Therefore, it can compare remote databases across a wide-area network. To minimize network usage, it separates data into chunks and calculates a checksum that is sent back to the source. Similarly, to minimize database overhead, it orders and processes data outside of the database. Furthermore, parallel threads are used to process tables simultaneously for improved performance.
Why Do Data Differences Occur?
It’s possible for differences in data to occur for the following causes:
- Hardware or database experiences failure
- Replication is configured incorrectly
- Operational activity causes corruption by accident
Why Verify Data?
Here are some reasons businesses require verification of their data:
- Accuracy for critical business data
- Compliance with regulations, such as Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
- Audit of controls for certification, such as Service Organization Control Type 2 (SOC 2)
Use Data with Confidence
Compare and repair compliments database replication by verifying that data is a reliable source of information for insights, analytics, and intelligence. Incomplete or incorrect data can have real-world implications on a business. In healthcare, it could make a mistake with patient care. In retail, it could make a mistake in expansion. In finance, it could violate a sanctions list. Error-free data that has been verified is a good step towards data that it is useful and actionable.

















